Explain How Opportunity Cost Differs From Money Cost
Conversely the opportunity cost is defined as the cost of opting one course of action and forgoing another opportunity to undertake that course of action. With the figures from the formula.
Difference Between Opportunity Cost And Trade Off Difference Between
These costs calculate the missed opportunity and calculate income that we can earn by following some other policy.

. Trade-off refers to all the other alternatives which are foregone to do what we want. The opportunity cost is time spent studying and that money to spend on something else. Opportunity cost and the PPC.
On the contrary the opportunity cost is the expected return on an investment other than the existing one. For example the entrepreneur could have earned a salary had he worked for others instead of spending time on his own business. An opportunity cost is the value of the next best alternative.
Opportunity cost 32000 - 35000. While opportunity cost is usually expressed in terms of money as was done in the example of the student studying economics it can also be done in term of hours spent or. Opportunity cost Potential value of option not chosen Actual value of option chosen.
If you decide to spend money on a vacation and you delay your homes remodel then your opportunity cost is the benefit living in a renovated home. This means you would lose 3000 if you stay at your current job. Explicit costs are costs that require a money payment.
C Provide an example of a business practice with an opportunity cost that is different than its accounting cost. PV 1200 1061 1131. The concept of opportunity cost does not apply to those goods and services which are produced without money cost.
The opportunity cost is planting a different crop or an alternate use of the resources land and farm equipment. Money costs are the actual cash or credit costs that an entity incurs during its business operations. For example if a business invests a significant amount of time into non-profit work the implicit cost would be the money earned or lost by spending time volunteering rather than working.
As you can see from the above the concept of opportunity cost may be applied to many different situations and arises when we need to make a choice between different alternatives. Opportunity cost measures the impact of making one economic choice instead of another. If your interest rate assumption for the 3 years is accurate you would be better off waiting for the 1200 payment in the future rather than taking 1000 today.
The major difference between sunk cost and opportunity cost is that when the organizations are making important strategic decisions for their future sunk cost must not be considered as it incurred in the past and cannot be recovered. Investing in Company B would have netted you 1500. Implicit costs are costs that do not require a money payment.
Opportunity cost represents the quantum of profit that is let go when an entity chooses one resource utilization alternative over another. Implicit opportunity cost. Production Possibilities Curve as a model of a countrys economy.
Opportunity cost and the PPC. Opportunity cost is the value of what you lose when you choose from two or more alternatives. Often money becomes the root cause of decision-making.
A Explain how opportunity cost differs from accounting cost. The opportunity cost includes both explicit and implicit costs. These costs fail to take into account the element of inertia.
PV FV 1 interest ratenumber of periods In our example the present value of 1200 in three years is. Its necessary to consider two or more potential options and the benefits of each. This is the currently selected item.
Costa Rica a developing nation holds a National debt of 3000 billion and requires paying an interest bill on the national debt that amounts to. Opportunity cost can be considered while making decisions but its most accurate when comparing decisions that have already been made. B Does every economic choice in business have an opportunity cost.
The eight key points of difference between opportunity cost and money cost are as follows. Lets explain the same with the help of an example. Youd plug those numbers into the formula like so.
Thus the opportunity cost of this choice is 500. But in fact they are heterogeneous which falsifies the concept of opportunity cost. This type of opportunity cost is an intangible cost that cannot be easily accounted for.
Opportunity costs are incomes from the next best alternative that is foregone when the entrepreneur makes certain choices. Opportunity cost -3000. If by default you could be earning 5 interest pa.
There are some who equate marginal cost with opportunity cost. Opportunity cost 1500 1000 500. Opportunity cost is the cost of taking one decision over another.
PPCs for increasing decreasing and constant opportunity cost. Opportunity costs apply to many aspects of life decisions. Opportunity cost examples can also be looked at from the point of view of a tradeoff as well between the choices foregone for the choice availed.
Howeverthe opportunity cost would be useful in deciding the best option that must be selected in making important decisions. At this stage you should know whether or not the financial gains outweigh the costs. This cost is not only financial but also in time effort and utility.
Opportunity cost can lead to optimal decision making when factors such as price time effort and utility are considered. It assumes that all the factors are homogeneous. An opportunity cost reflects the benefit forgone in order to do something else.
Lets say you decided to invest in Company A which nets you 1000. On your money invested in a bank term deposit but instead invest in something else or do something else entirely with the money your opportunity cost is that 5 in interest forgone. Opportunity Cost and Marginal Cost Opportunity cost is described as the sacrifice of the highest value of a good that one has to forego to obtain another while marginal cost is the cost incurred on producing an additional unit in a factory.
While its often used by investors opportunity cost can apply to any decision-making process. When you invest opportunity cost can be defined as. Opportunity cost Return on the option not chosen - Return on chosen option.
A sunk cost is money already spent in the past while opportunity cost is the potential returns not earned in the future on an investment. Make an informed decision. A farmer chooses to plant wheat.
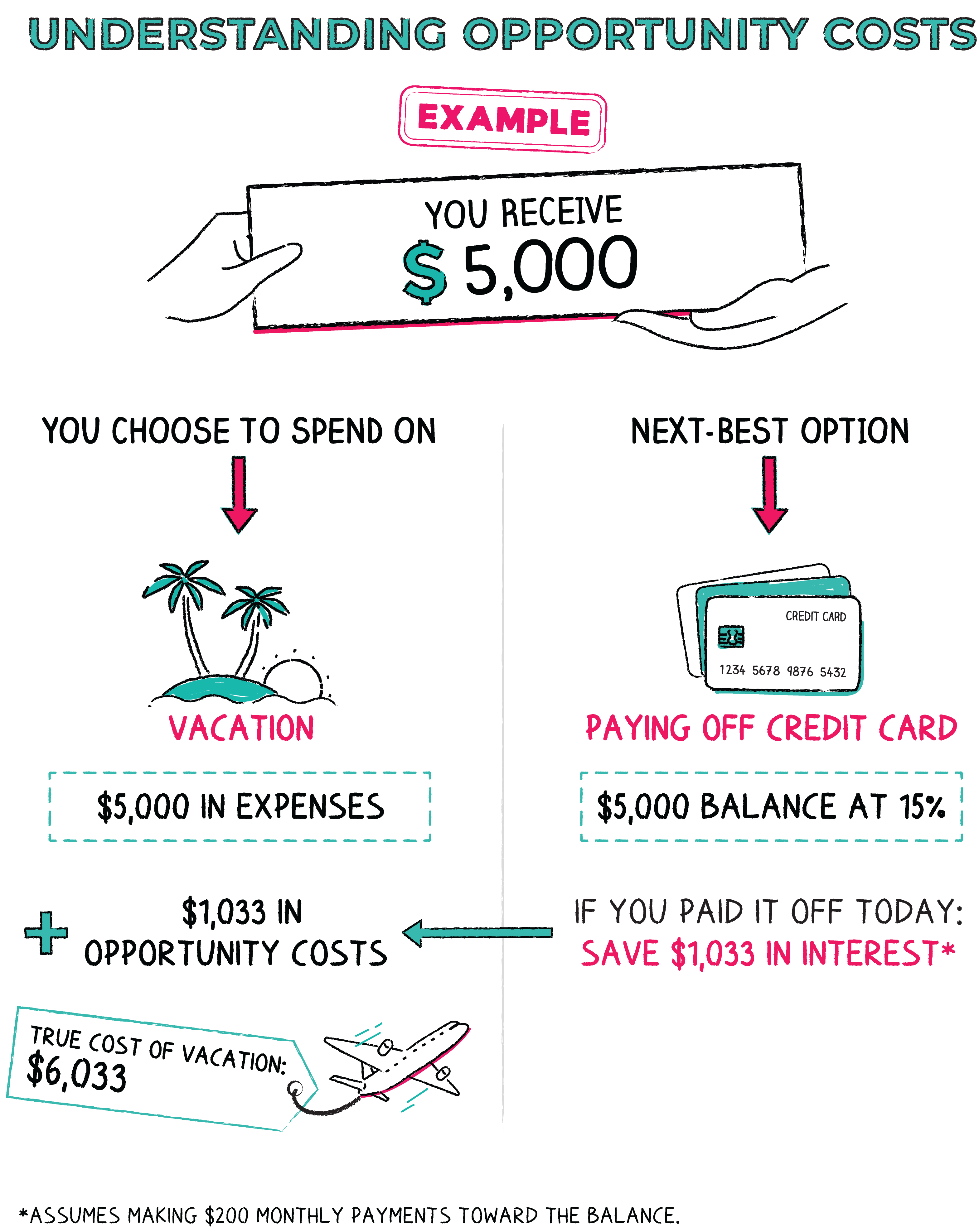
What Is Opportunity Cost Investment Opportunities Napkin Finance

Minimizing The Cost Of Living As A Working Mom Saving Money Budget Cost Of Living Show Me The Money

Opportunity Cost Can Be Defined Of The Loss Of Other Alternatives When One Alternative Is Chosen We Make These Deci Opportunity Cost Going To Work Budgeting

Opportunity Cost How To Introduce Opportunity Cost Economics Lessons Opportunity Cost Lesson

Opportunity Costs Something To Do Opportunity Cost Canning

Fitmoney For Grade 2 Spending Decisions Teacher Lesson Plans Opportunity Cost Financial Literacy

Opportunity Cost Flip Book If I Choose Opportunity Cost Third Grade Social Studies Teaching Economics

How To Stop Making Foolish Money Decisions Personal Finance Opportunity Cost Finance Advice

Opportunity Cost Formula Example Analysis Accountinguide

Opportunity Cost Definition 4 Examples Economics Boycewire

Opportunity Cost Meaning Importance Calculation And More
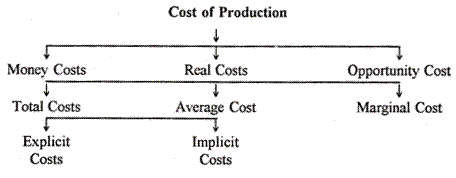
Cost Of Production Money Real And Opportunity Costs

This Comic Has Chapters On The Basic Steps Of One Economic Choice It Even Describes Opportunity Cost T Children S Literature Teaching Opportunities Comics

Difference Between Absolute And Comparative Advantage Definition Features And Characteristics Comparative Advantage Advantage Opportunity Cost
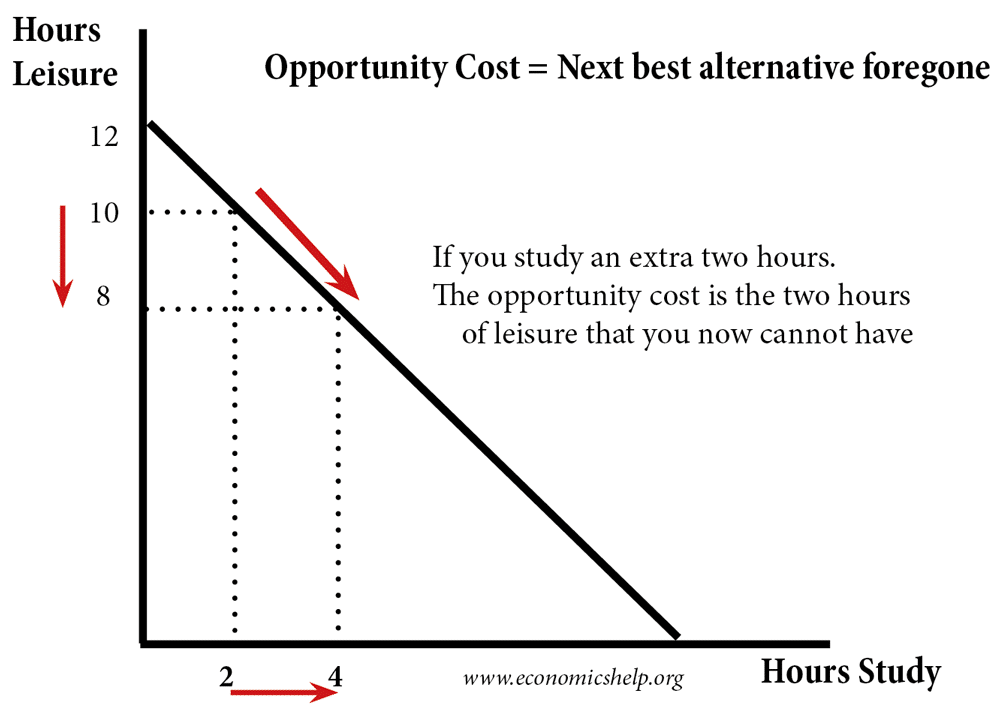
Opportunity Cost Definition Economics Help

Scarcity Choice And Opportunity Cost Lesson Opportunity Cost Opportunity Cost Lesson Economics Lessons

Cost Of Capital Cost Of Capital Opportunity Cost Financial Management


Comments
Post a Comment